If you’re familiar with non-fungible tokens (NFTs), you may have come across the term “floor price.” When buying NFTs, floor prices are something worthy of note, as they affect your purchase price.
So what are NFT floor prices, and how are they determined?
What Is an NFT Floor Price?
An NFT floor price is the minimum price at which a non-fungible token within a specific collection or on a marketplace can be bought or sold. They are benchmarks for gaining insight into the lowest or fairest price of an NFT.
These prices are updated in real-time and indicate the health and activity of the tokens. When NFT floor prices are relatively high and stable, it suggests a strong demand and prospering market. Conversely, when floor pricing is low or stagnant, it indicates a lack of interest or an oversaturated market.
NFT floor prices help you measure an NFT project’s market health, identify possible investment prospects, and estimate the long-term values of your holdings. Putting a specific value on NFTs can be tough, as they cannot be divided from their whole and are relatively new in the crypto industry.
How Is NFT Floor Price Calculated?
Calculating NFT floor pricing isn’t a science; NFT traders rely on market trends and historical data to calculate floor prices.
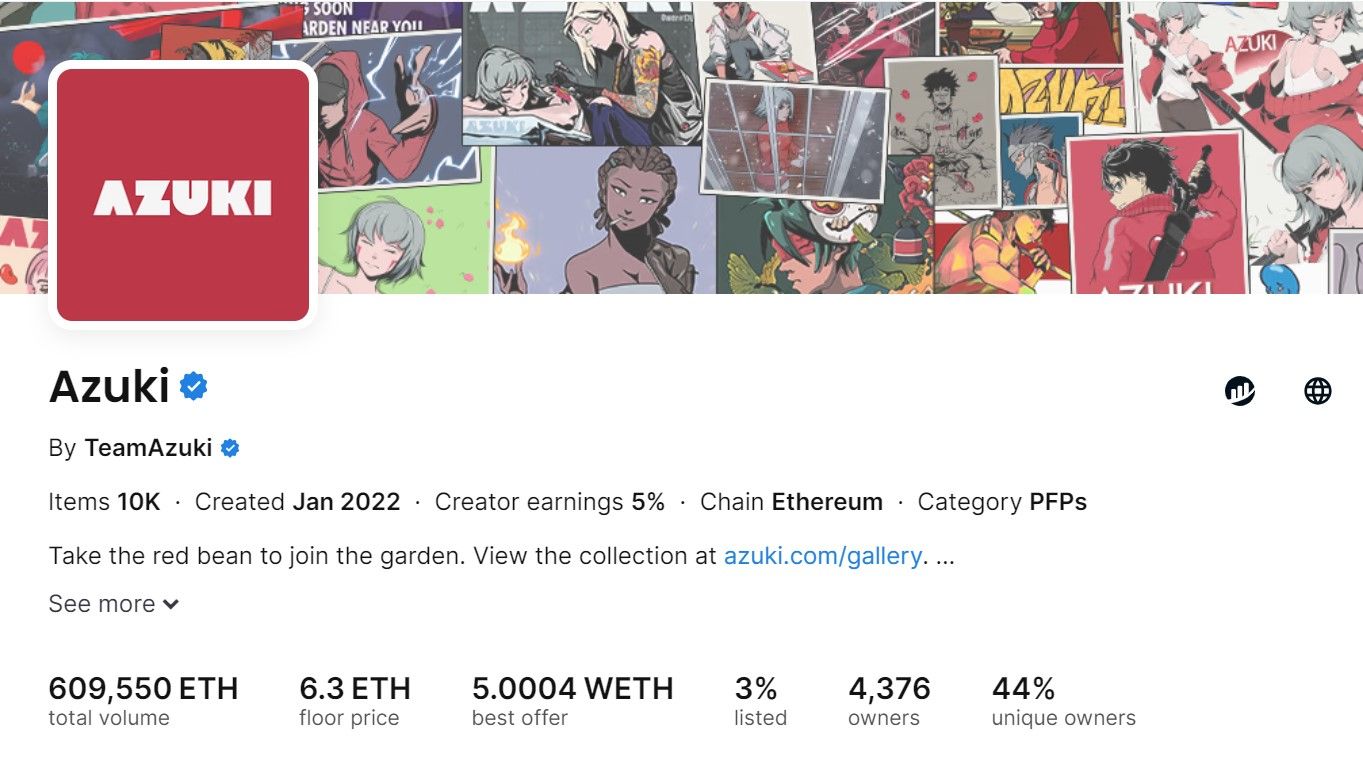
Many factors determine an NFT’s floor price. For example, popular NFT collections like Azuki have extremely high NFT floor prices. Due to Azuki’s’ popularity and desirability, it boasts a high NFT floor price, which indicates a stable and in-demand market—although this isn’t always the case.
Usually, when an NFT’s floor price is too high, some investors steer clear of the asset and instead purchase easily accessible tokens, hoping that they’ll pump in the future.
Typically, the following factors cause NFT floor prices to grow or remain stagnant.
1. Rarity and Scarcity
NFT collections with unique and scarce artistic attributes frequently command higher NFT floor prices. An NFT collection with limited editions will often have a higher demand than one without.
Also, the fewer the NFTs in a collection, the higher the potential value and demand of each piece.
2. Popularity and Demand
The demand and interest for a specific NFT collection greatly influence its floor price. Similarly, if the creator of the NFT collection is well-known, the floor price will also be positively affected. High-profile NFT collections associated with renowned brands or creators attract higher values due to popularity.
3. Utility and Desirability
Some NFTs have access to great utilities, which give them an edge and boost their floor price. Granting access to exclusive content or experiences is an example of a high-value NFT utility. These utilities can cause higher floor prices.
Additionally, perceived desirability or longing for an NFT can also determine its floor price.
Can You Buy an NFT Below Its Floor Price?
NFT floor prices represent a seller’s minimum price. However, this doesn’t restrict you from negotiating prices or making offers. Some sellers may be open to negotiations and accept offers below the floor price.
Most times, this is because the NFT collection isn’t highly requested and has been listed for a long time without any purchase. Other times it could be because some sellers are motivated to sell out fast.
You should, however, note that buying an NFT below its floor price may not be easy. In highly liquid NFT markets with strong demand, many sellers are reluctant to accept any offer below the floor price.
Understanding NFT Floor Prices
NFT floor prices are vital, offering NFT traders a reference point for assessing value.
Many factors, including popularity and desirability, influence floor prices. Understanding the dynamics of NFT floor prices helps you make informed industry decisions and identify potential investment opportunities.
Credit: Source link

.jpg)



 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  XRP
XRP  Solana
Solana  USDC
USDC  TRON
TRON  Lido Staked Ether
Lido Staked Ether  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  Cardano
Cardano  Figure Heloc
Figure Heloc  WhiteBIT Coin
WhiteBIT Coin  Wrapped stETH
Wrapped stETH  Wrapped Bitcoin
Wrapped Bitcoin  Zcash
Zcash  Hyperliquid
Hyperliquid  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  Chainlink
Chainlink  USDS
USDS  Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)
Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)  LEO Token
LEO Token  Stellar
Stellar  WETH
WETH  Wrapped eETH
Wrapped eETH  Ethena USDe
Ethena USDe  Litecoin
Litecoin  Monero
Monero  Coinbase Wrapped BTC
Coinbase Wrapped BTC  Hedera
Hedera  Avalanche
Avalanche  Sui
Sui  Shiba Inu
Shiba Inu  Uniswap
Uniswap  Dai
Dai  Polkadot
Polkadot  Ethena Staked USDe
Ethena Staked USDe  Toncoin
Toncoin  Cronos
Cronos  USDT0
USDT0  World Liberty Financial
World Liberty Financial  sUSDS
sUSDS  MemeCore
MemeCore  Mantle
Mantle  PayPal USD
PayPal USD  Canton
Canton  Bittensor
Bittensor  NEAR Protocol
NEAR Protocol  USD1
USD1